Tesla makes electric vehicles, which are environmentally friendly as they do not produce tailpipe emissions. However, these electric vehicles use batteries that get old and need to be scrapped. When not disposed of correctly, they can cause environmental pollution or even pose a fire risk.
With millions of Tesla cars already sold, and the company aiming to increase production by 50% yearly, there will soon be a lot more Tesla cars on the road. The company needs to plan for end-of-life for its batteries if the environmental conservation goals of Elon Musk are to be met.
This article looks into how Tesla batteries age and the methods the American company uses to handle its batteries when they are no longer fit for use in EVs
How do Tesla batteries age?
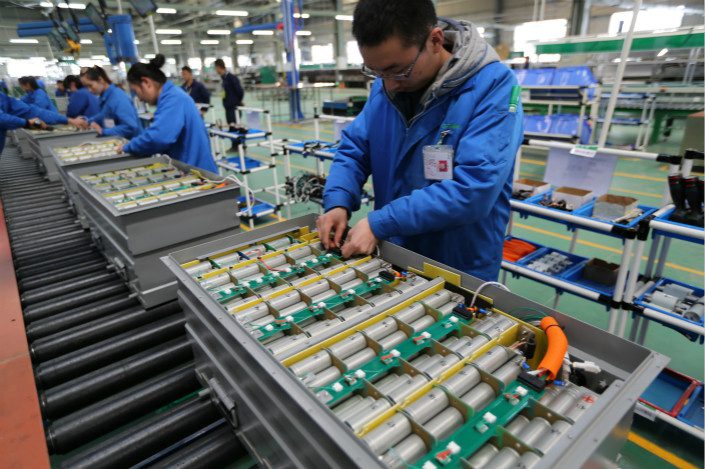
Tesla made the lithium-ion battery and electric vehicles trendy with its Roadster performance car. The electric car was able to achieve more than 200 miles, a key milestone at the time. Until recently, Tesla cars have used Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) battery chemistry, but some Model 3’s made in China now come with Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) chemistry
Some of the about 2,500 Roadsters made by Tesla are still on the road, although they would have less range if the owners have not replaced the batteries.

This reduction in driving range is due to battery degradation, which affects batteries as they age. Degradation is believed to be accelerated by frequent DC fast charging.
In its 2020 Impact Report, Tesla claims its cars have some of the best battery capacity retentions in the industry. The average Tesla car retains about 90% of its original capacity after 200,000 miles.
This means the battery experiences a 1% capacity loss per 20 km driven. Also, assuming a full cycle of 250 km, the battery would have passed through 800 charging and discharging cycles.
Another interesting fact is that American drivers dispose of their cars after 200,000 miles on average. In Europe, cars are disposed of faster at 150,000 km. These figures show a Tesla battery can outlive the vehicle, although EVs would typically last longer than their ICE counterparts due to breaking down less often.
Regardless of how long they last, the time will come when a Tesla battery has to be replaced. How does Tesla handle the old batteries?
What happens to Tesla battery packs when they reach their end of life?
Tesla claims on its website that the materials in its lithium-ion battery are recoverable and recyclable. When they reach end-of-life, the battery materials are refined and put into a new cell that is used in a new battery pack. The battery pack powers a new Tesla car until the next recycle before they end up in another vehicle.
How efficient is Tesla’s battery recycling process?
The company claims it 100% of its scrapped batteries are recycled, and none ends up in landfills.
The company has set up its own ecosystem to make new batteries from the old batteries it retrieves. The goal is to attain a closed-loop system.
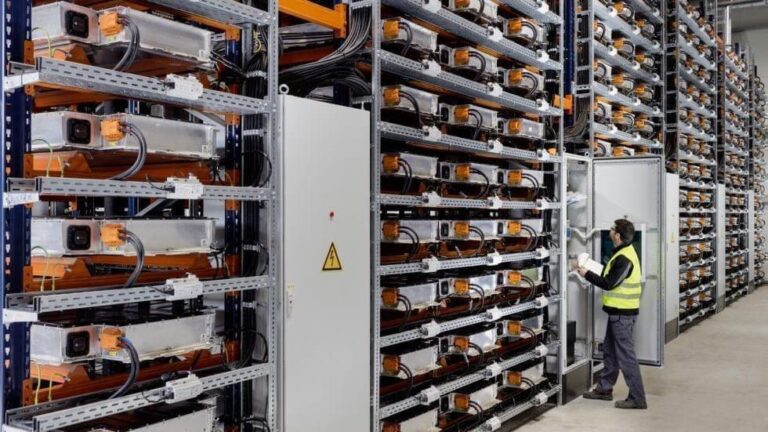
Tesla chose to handle the recycling in-house rather than rely on third parties to be able to scale up as required. For now, most of the batteries Tesla deals with are still pre-consumer, as the majority of the cars it has made are still roadworthy, and their batteries are still going strong. However, Tesla is laying the groundwork for what will become a full-blown operation.
Part of this groundwork involves adding recycling facilities to its battery plants. These include Gigafactory Berlin and Gigafactory Texas.
Back in July 2021, Tesla applied for a patent on recovering undamaged and unutilized nickel and cobalt, which are two critical raw materials in modern battery cells. The process uses electrochemical dissolution to recover these two materials. This patent is a big deal because it will help Tesla cut its expenditures for sourcing materials, alongside preventing the battery components from going to landfills. And while Tesla would prefer to move away from cobalt due to its controversial origin, this is the next best possible outcome.
“Our goal is to develop a safe recycling process with high recovery rates, low costs, and low environmental impact. From an economic perspective, we expect to recognize significant savings over the long term as the costs associated with large-scale battery material recovery and recycling will be far lower than purchasing additional raw materials for cell manufacturing.”
Tesla 2020 Impact Report
In late 2020, Tesla was issued a fine by German authorities relating to its old battery management. In the country, auto manufacturers are obligated to take back batteries to dispose of them environmentally friendly. However, Tesla’s German subsidiary clarified the fine was related to administrative requirements or reporting, as the company accepts battery packs. It is fighting the 12 million euro fine.
Tesla, however, tries to extend the battery’s life before recycling. It believes prolonging life is superior and more beneficial to the environment, making the company try everything to keep each battery pack it receives working through servicing. This can be done at any of Tesla’s service centers around the world.
What about Tesla’s battery energy storage system business?
Tesla sells domestic energy storage products like the Powerwall. It also sets up large-scale energy storage systems like the one located in South Australia. It has an initial 100 MW capacity that can power 30,000 homes at peak output.

However, unlike companies like Lucid that want to repurpose their end-of-life batteries in energy storage systems, Tesla seems to prefer recycling. Back in 2016, its then Chief Technical Officer, JB Straubel, who was the company’s battery expert, said Tesla had looked at the option closely but concluded it was not an economical or excellent use of Tesla’s assets.
Incidentally, Straubel has left Tesla and is running startup Redwood Materials, which focuses on recycling electric vehicle batteries and operates a plant in Carson City, Nevada. It recently completed another round of funding and signed an agreement with Ford to recycle its batteries.
Tesla batteries managed sustainably?
Most of the batteries made by Tesla are still working very well and retain high capacity even after many years. However, the company is preparing to responsibly handle the millions of EV batteries that will reach end-of-life in the future by making investments in battery recycling. It has created connected ecosystems from manufacturing, service and energy storage to address the challenges posed by the mass production of Electrical Vehicles reliant on Lithium-ion batteries.