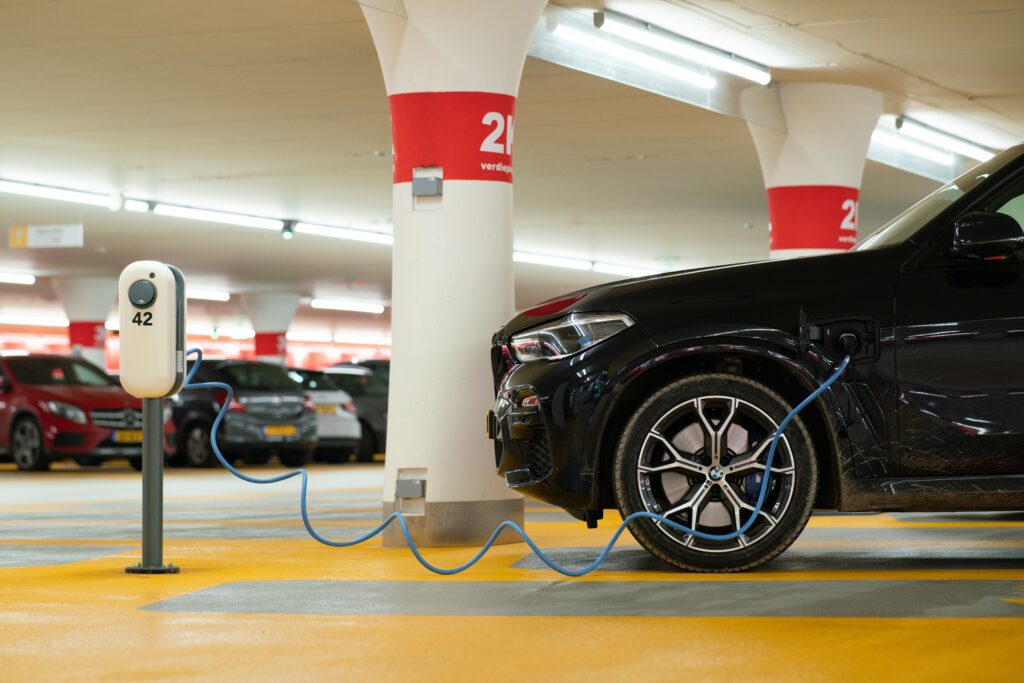
If you are considering buying an electric car but are on a tight budget, you may consider going down the more affordable route by purchasing a used EV. However, before you sign the purchase agreement, you might need to consider an aspect of owning a car , namely: a warranty. Depending on the age or mileage on the clock you may need an extended warranty.
New cars come with a manufacturer warranty, but many used vehicles are no longer covered. This is where an extended warranty comes in. For internal combustion engine cars, this is an established practice. However, when it comes to electric vehicles, it is a new concept, and there is a lot of confusion about it. In this article, we dive into what an extended warranty means for a used electric car.
What is an extended warranty?
When you buy a new car, the manufacturer undertakes to pay for some repairs or part replacements that occur within a certain period or driven miles. This gives car owners peace of mind as cars are mechanical implements that can break down anytime. For EVs this is typically 8 years or 160,000 kilometres, whichever comes first.
However, while buying a used car is a cheaper route to car ownership, it usually means the manufacturer’s warranty no longer applies. This means you have to pay for any required repairs out of your own pocket.
For traditional cars, this can be addressed by purchasing an extended warranty on a used car. It could come from the car maker or a third party. This is regardless of the car’s age or mileage.
EVs are relatively new; many electric vehicles are still under warranty or with the original buyers. However, as the pool of older electric vehicles grows, spurring a used-EV market, the auto industry will need to find a way to offer extended warranty cover.
However, since electric cars are known to be more reliable and require less maintenance, do you need an extended warranty?
Why do you need one for a used electric car?
When listing the advantages of electric cars, being relatively maintenance-free often comes top. This reliability is due to the absence of the internal combustion engine, a complex component with many parts that can break down. However, electric cars sometimes need repairs.
For example, your used electric car has many electric components and circuitry that can stop working. Your Tesla car will be difficult to operate if the central touchscreen console stops working, and you are looking at a bill of over a thousand dollars to replace it. The air conditioning might break, and you will need to go for a repair to avoid baking or freezing inside your car.
Your used EV relies on the battery to work and, as a crucial component, must be replaced when faulty. These batteries are built to last, with many features to keep them working for as long as possible. However, it is accepted that the lithium-ion battery powering your car will degrade and gradually lose capacity until it can no longer work. Sometimes, it just becomes faulty. EV batteries are costly, and replacing them is a significant expense that can cost up to $20,000. This value could well be substantially above what you paid for the car in the first place.
What does an extended warranty for used electric cars look like?
When considering purchasing an extended warranty, it is important to understand the parts of your used EV that should be covered. As the battery is one of the most expensive and important components, it is vital the battery is covered under the policy. However, there are other major parts worthy of coverage.
The electric motor is also essential. Even though reliable, electric motors are usually included in a comprehensive warranty. Your warranty may also cover parts, drive shafts, bearings, etc., for failure and not necessarily wear.
Other parts of your used EV that an extended warranty should cover include the inverter (which turns the DC from the battery into the AC that the electric motor can use) and the power control module (PCM) that decides the amount of power that goes to different parts of the car.
You should also include the reduction gears if your used EV has an electronic drive unit that combines the motors, inverter, PCM, and reduction drive as a single unit. This simplifies the design and manufacturing process but drives up repair costs in case of failure.
Other important components that should be included in your extended warranty include the charging system. They are usually complicated because of their job description and could cost you a small fortune to repair or replace.
Where can you get an extended warranty for your used electric car?
As mentioned earlier, an extended warranty could be provided by the car maker or a third party. However, because EVs are relatively new, they do not have the same level of extended warranty support.
If you purchase a used Tesla EV, you may purchase an extended warranty from the company. However, there are some terms and conditions that you need to keep an eye on. For example, you can only buy an extended warranty within 30 days or 1,000 miles of the original warranty expiring. Once that window closes, you cannot get it from the EV maker. However, you can inherit the original warranty of a Tesla car if you buy it from the owner directly and not through a dealer.
If you cannot get an extended warranty from the car maker, you can approach a handful of third-party companies like Motor Easy in the UK that can provide coverage for you, including the battery.
When purchasing an extended warranty, the level of coverage is determined after your car has been inspected.
Conclusion
The market for used electric cars is still young, but it is important to consider getting an extended warranty when purchasing one. It will protect you from getting overwhelming repair bills while operating the car.